Introduction to Lathes: An Overview
Lathes are widely used machines in various manufacturing and repair shops to process rotating surfaces such as shafts, discs, and sleeves. These machines are among the most essential tools in the mechanical manufacturing industry. Their ability to perform a variety of operations makes them indispensable. From basic turning to advanced CNC lathes, these machines have been integral in shaping the modern manufacturing process.
In this article, we will explore the different classifications of lathes, focusing on CNC (Computer Numerical Control) lathes, and discuss their various types, functions, and applications in modern industry.
What is a Lathe?
A lathe is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece against a cutting tool to shape it. This process can be used to create cylindrical, conical, or spherical shapes, or even complex geometries such as threads. The versatility of lathes makes them essential in fields like metalworking, woodworking, and manufacturing.
Basic Components of a Lathe
- Bed: The base of the lathe, providing support and alignment for all the components.
- Headstock: Contains the spindle that holds the workpiece.
- Tailstock: Provides support for the other end of the workpiece during turning.
- Carriage: Holds the cutting tool and moves it along the workpiece.
- Tool Post: Where the cutting tools are mounted.
Types of Lathes
Lathes can be categorized in various ways based on their construction, operation, and the kind of work they are designed for. Let’s take a closer look at these classifications.
CNC Lathe Classifications
CNC lathes are automatic machines that are capable of executing complex tasks with high precision. They are classified primarily into horizontal and vertical categories.
Horizontal CNC Lathes
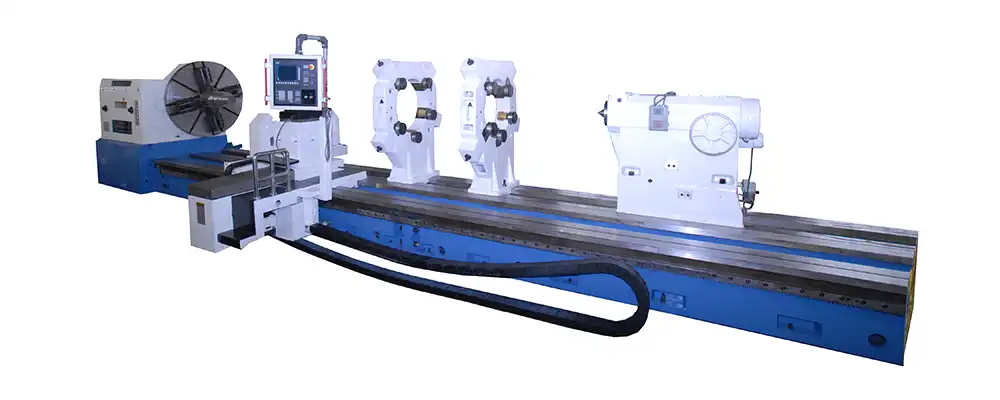
Horizontal CNC lathes feature a spindle aligned parallel to the ground, which is common in the industry. These machines are ideal for machining large, heavy workpieces and are known for their stability and efficiency.
Advantages of Horizontal CNC Lathes
- Greater rigidity and strength.
- High-speed production capabilities.
- Easy chip removal due to the horizontal axis.
Vertical CNC Lathes
Vertical CNC lathes, on the other hand, have a vertically aligned spindle. These lathes are best suited for machining large and complex parts that require more precise movements.
Advantages of Vertical CNC Lathes
- Improved access to large workpieces.
- Better cooling and chip removal.
- Suitable for small to medium-sized parts.
Key Features of CNC Lathes
Both horizontal and vertical CNC lathes share some common features, such as:
- Precision and Automation: CNC lathes use computerized controls to perform highly accurate machining tasks.
- Multi-Axis Control: These lathes often feature at least two axes, with higher-end models offering additional axes for more complex operations.
- Increased Efficiency: CNC technology reduces the need for manual labor, allowing faster and more accurate production.
Single vs. Dual Turret CNC Lathes
Another distinction in CNC lathes is whether they have a single turret or a dual turret.
- Single Turret CNC Lathe: Uses one toolholder that rotates to present various tools.
- Dual Turret CNC Lathe: Features two turrets, allowing more tools to be mounted, and thus, performing more complex operations simultaneously.
How CNC Lathes Improve Efficiency
One of the biggest benefits of CNC lathes is their ability to automate processes. This reduces the need for human intervention, speeds up production, and enhances the precision of machining tasks. Some of the key aspects where CNC lathes excel include:
- Multi-axis machining: CNC lathes can operate on more than two axes, allowing for intricate shapes and designs.
- Automation: The ability to program the machine to automatically perform various operations such as turning, drilling, and threading.
- Error Reduction: CNC systems are less prone to human error, leading to higher consistency in the final product.
Types of CNC Lathes Based on Spindle Position
Lathes can be categorized based on the position of their spindle, and there are two main types:
Vertical CNC Lathe
The vertical CNC lathe’s spindle is oriented perpendicular to the horizontal plane. The workpiece is mounted on a rotating circular table, and the cutting tool moves vertically. These lathes are ideal for working with large, heavy components.
Horizontal CNC Lathe
In this design, the spindle is horizontal, and it rotates the workpiece along a straight path. Horizontal lathes are typically better for precision cutting, especially for parts with a long axial length.
Lathe Types Based on Functionality
Lathes are also classified according to the type of work they are meant to perform. Some of the most common types include:
Chucking Lathes
These lathes use a chuck to hold the workpiece in place while it is being turned. Chucking lathes are used primarily for smaller workpieces.
Center Lathes
A more traditional form of the lathe, center lathes are used for a wide variety of materials and shapes. They are versatile and can be used for tasks like turning, facing, and threading.
Turret Lathes
These lathes are similar to the center lathe but come with a turret tool post that holds multiple tools. This feature allows for the continuous production of parts with a variety of operations.
Automatic Lathes
Automatic lathes can perform multiple tasks without human intervention, improving efficiency, and reducing labor costs. They are commonly used for mass production of small parts.
Lathe Types Based on Operational Mechanism
Manual Lathes
These lathes require manual operation by an operator. While they are slower and less precise than CNC lathes, they are still used in situations where high flexibility is required.
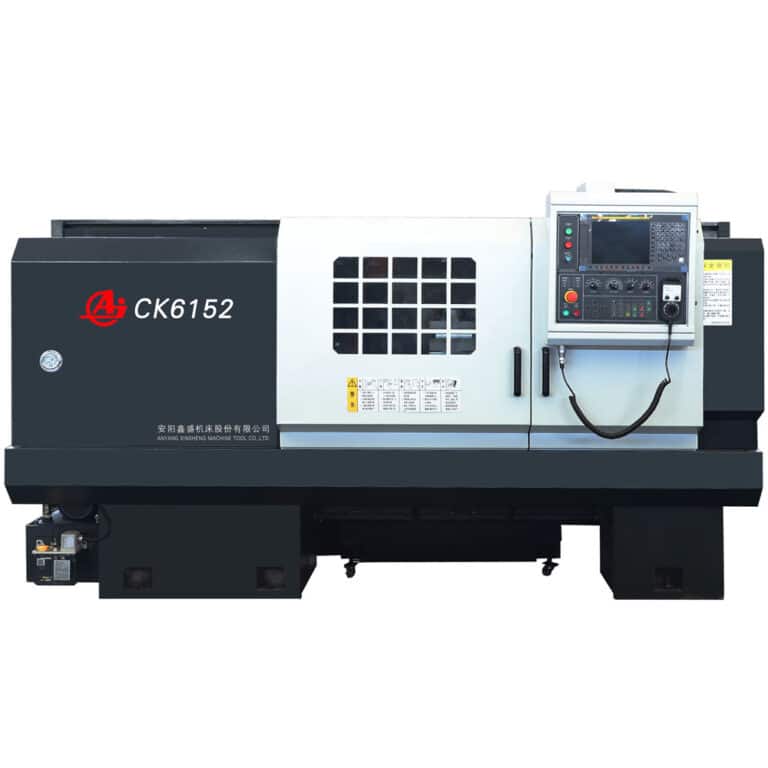
CNC Lathes
CNC lathes use a computer to automate the process, making them faster and more accurate than manual machines. These lathes can perform a wider range of tasks without needing an operator to adjust them manually.
Conclusion: The Evolution of Lathes in Manufacturing
Lathes have undergone significant advancements over the years, evolving from simple machines to sophisticated, computer-controlled devices that can perform a wide range of tasks. Whether it’s a manual lathe or a high-tech CNC version, the lathe continues to play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing. With their ability to process complex shapes and maintain high levels of precision, CNC lathes are now integral to industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a CNC lathe and a traditional lathe?
A CNC lathe is computer-controlled, making it more precise and efficient than traditional manual lathes. It can handle more complex tasks and reduce human error.
2. Can CNC lathes be used for all materials?
Yes, CNC lathes can handle a variety of materials including metals, plastics, and composites. The machine’s parameters can be adjusted to suit the material being processed.
3. How does a CNC lathe improve manufacturing efficiency?
By automating the turning process, CNC lathes reduce the need for manual labor, increase precision, and allow for faster production cycles.
4. Are CNC lathes expensive?
Yes, CNC lathes can be expensive, especially when compared to traditional machines. However, their ability to improve production efficiency and reduce labor costs can make them cost-effective in the long run.
5. What industries use CNC lathes?
CNC lathes are used in a wide variety of industries including aerospace, automotive, electronics, and medical equipment manufacturing.